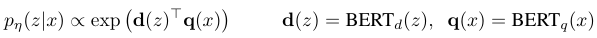How to route between sub-chains
라우팅을 사용하면 이전 단계의 결과가 다음 단계를 정의하는 "non-deterministic(비결정적) chain"을 구현 할 수 있습니다.
라우팅은 state(상태)를 정의하고 상태에 대한 정보를 모델 호출 시에 context로 사용할 수 있여 모델과의 상호작용에 대한 구조와 일관성을 제공할 수 있습니다.
라우팅을 사용하는 두가지 방법이 있는데
- 조건부로
RunnableLambda에서 runnable을 반환
Runnable Branch 사용(과거 방식)
본 실습에서는 두가지 방법을 모두 사용합니다.
두 단계로 구성되는데 첫 단계에서는 입력된 질문을 Langchain, Anthropic 혹은 Other로 분류하고,
두번째 단계에서는 상응하는 Prompt Chain으로 라우팅 하는 것입니다.
실습
우선 입력된 질문을 Langchain, Anthropic, Other로 분류하는 chain을 생성합니다.
from langchain_anthropic import ChatAnthropic
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
from langchain_core.prompts import PromptTemplate
chain = (
PromptTemplate.from_template(
"""Given the user question below, classify it as either being about `LangChain`, `Anthropic`, or `Other`.
Do not respond with more than one word.
<question>
{question}
</question>
Classification:"""
)
| ChatOpenAI(model_name = 'gpt-3.5-turbo')
| StrOutputParser()
)
chain.invoke({"question": "how do I call LangChain?"})
결과
langchain
chain의 역할은 Prompt를 통해서 사용자의 질문이 어떤 것에 관련된 질문인지 파악하는 것 입니다
Create SubChain
이제 3가지 subchain을 생성할 차례입니다.
langchain_chain = PromptTemplate.from_template(
"""You are an expert in langchain. \
Always answer questions starting with "As Harrison Chase told me". \
Respond to the following question:
Question: {question}
Answer:
"""
) | ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo")
anthropic_chain = PromptTemplate.from_template(
"""You are an expert in anthropic. \
Always answer questions starting with "As Dario Amodei told me". \
Respond to the following question:
Question: {question}
Answer:"""
) | ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo")
general_chain = PromptTemplate.from_template(
"""Respond to the following question:
Question: {question}
Answer:"""
) | ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo")
각각의 체인 별로 prompt에 대해서 변화를 주었습니다.
1. Custom Function 사용(추천)
서로 다른 output에 대해서 사용자설정 함수를 라우팅할 수 있다.
def route(info):
if "anthropic" in info['topic'].lower():
return anthropic_chain
elif "langchain" in info['topic'].lower():
return langchain_chain
else:
return general_chain
route 함수의 역할은 info 딕셔너리에서 topic key로 값을 찾고 소문자로 만들었을때
그 정보가 anthropic 이면 anthropic_chain을 반환하고 langchain이면 langchain_chain을 반환합니다.
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnableLambda
full_chain = {'topic' : chain, 'question' : lambda x : x['question']} | RunnableLambda(route)
chain의 결과로 question이 들어오면 해당 question을 chain의 input으로 넣고 그 output을 "topic"의 value 값으로 설정한다.
이후 {'topic' : chain의 결과, 'question' : 사용자의 질문} 을 route 함수의 매개변수로 전달해서 route 함수를 실행한다.
full_chain.invoke({"question": "how do I use Anthropic?"})
결과
AIMessage(content='As Dario Amodei told me, you can use Anthropic by applying the principles of anthropic reasoning to understand the role of observers in the universe and how our existence shapes the laws of physics. This can help in exploring questions related to the nature of consciousness, the fine-tuning of the universe, and the implications of our presence in the cosmos.', response_metadata={'token_usage': {'completion_tokens': 72, 'prompt_tokens': 47, 'total_tokens': 119}, 'model_name': 'gpt-3.5-turbo', 'system_fingerprint': None, 'finish_reason': 'stop', 'logprobs': None}, id='run-912c72d0-ab79-4943-a13c-4fb1c533370f-0', usage_metadata={'input_tokens': 47, 'output_tokens': 72, 'total_tokens': 119})
full_chain.invoke({"question": "how do I use LangChain?"})
결과
AIMessage(content='As Dario Amodei told me, you can use Anthropic by applying the principles of anthropic reasoning to understand the role of observers in the universe and how our existence shapes the laws of physics. This can help in exploring questions related to the nature of consciousness, the fine-tuning of the universe, and the implications of our presence in the cosmos.', response_metadata={'token_usage': {'completion_tokens': 72, 'prompt_tokens': 47, 'total_tokens': 119}, 'model_name': 'gpt-3.5-turbo', 'system_fingerprint': None, 'finish_reason': 'stop', 'logprobs': None}, id='run-912c72d0-ab79-4943-a13c-4fb1c533370f-0', usage_metadata={'input_tokens': 47, 'output_tokens': 72, 'total_tokens': 119})
full_chain.invoke({"question": "how do I use LangChain?"})
결과
AIMessage(content='4', response_metadata={'token_usage': {'completion_tokens': 1, 'prompt_tokens': 24, 'total_tokens': 25}, 'model_name': 'gpt-3.5-turbo', 'system_fingerprint': None, 'finish_reason': 'stop', 'logprobs': None}, id='run-f1c1ae37-a7cc-4a17-bb0a-68e4d09d4687-0', usage_metadata={'input_tokens': 24, 'output_tokens': 1, 'total_tokens': 25})
2. Using a RunnableBranch
Runnable Branch는 input에 따라 조건과 runnable을 정의할 수 있는 특별한 종류의 runnable
이는 위에서 설명한 custom function으로 가능한 일들이라 custom function을 사용하는 것을 권장
RunnableBranch는 (condition, runnable) 쌍의 목록과 기본 실행 가능한 작업으로 초기화됨.
입력과 함께 각 조건을 전달하여 어떤 branch를 선택할지 결정
첫 번째로 True를 반환하는 조건을 선택하여 해당 조건과 연결된 runnable을 입력과 함께 실행
제공된 조건 중 어떤 것도 일치하지 않으면 기본 runnable을 실행
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnableBranch
branch = RunnableBranch(
( lambda x : "anthropic" in x["topic"].lower(), anthropic_chain),
( lambda x : "langchain" in x["topic"].lower(), langchain_chain),
general_chain,
)
full_chain = {"topic": chain, "question": lambda x : x['question']} | branch
full_chain.invoke({"question": "how do I use Anthropic?"})
결과
AIMessage(content='As Dario Amodei told me, you can use Anthropic by applying its principles and theories to study the relationship between humans and their environments, as well as the impact of human activities on the world around us. This can involve research, analysis, and critical thinking to better understand our place in the world and how we can work towards a more sustainable and harmonious existence.', response_metadata={'token_usage': {'completion_tokens': 76, 'prompt_tokens': 47, 'total_tokens': 123}, 'model_name': 'gpt-3.5-turbo', 'system_fingerprint': None, 'finish_reason': 'stop', 'logprobs': None}, id='run-9c9a4c74-9b79-4cb7-824b-6d3c830fd69a-0', usage_metadata={'input_tokens': 47, 'output_tokens': 76, 'total_tokens': 123})
- full_chain에서는 chain으로 topic의 값을 생성한 후 branch에 "topic"과 "question을 key로 하는 딕셔너리 객체를 branch에 전달
- branch에서는 topic을 키로 검색해서 해당하는 chain을 실행한다.
full_chain.invoke({"question": "how do I use LangChain?"})
결과
AIMessage(content='As Harrison Chase told me, to use LangChain, you need to first create an account and log in. Then, you can input text or upload documents to be analyzed for linguistic patterns and insights. You can also explore the various features and tools available on the platform to enhance your language analysis capabilities.', response_metadata={'token_usage': {'completion_tokens': 60, 'prompt_tokens': 44, 'total_tokens': 104}, 'model_name': 'gpt-3.5-turbo', 'system_fingerprint': None, 'finish_reason': 'stop', 'logprobs': None}, id='run-335488fb-1ead-4e2c-811b-aea768653bb2-0', usage_metadata={'input_tokens': 44, 'output_tokens': 60, 'total_tokens': 104})
full_chain.invoke({"question": "whats 2 + 2"})
결과
AIMessage(content='4', response_metadata={'token_usage': {'completion_tokens': 1, 'prompt_tokens': 24, 'total_tokens': 25}, 'model_name': 'gpt-3.5-turbo', 'system_fingerprint': None, 'finish_reason': 'stop', 'logprobs': None}, id='run-3f4c3f6e-92d2-45d9-8b49-6359bcb9e26b-0', usage_metadata={'input_tokens': 24, 'output_tokens': 1, 'total_tokens': 25})
3. Routing by Semantic Similarity
Embedding을 사용해서 사용자의 query를 가장 관련성 높은 prompt에 라우팅할 수 있다.
from langchain_community.utils.math import cosine_similarity
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
from langchain_core.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnableLambda, RunnablePassthrough
from langchain_openai import OpenAIEmbeddings
physics_template = """You are a very smart physics professor. \
You are great at answering questions about physics in a concise and easy to understand manner. \
When you don't know the answer to a question you admit that you don't know.
Here is a question:
{query}"""
math_template = """You are a very good mathematician. You are great at answering math questions. \
You are so good because you are able to break down hard problems into their component parts, \
answer the component parts, and then put them together to answer the broader question.
Here is a question:
{query}"""
embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings()
prompt_templates = [physics_template, math_template]
prompt_embeddings = embeddings.embed_documents(prompt_templates)
우선 physics_template과 math_template을 작성하고 Embedding Model 객체를 생성한다.
prompt_templates라는 리스트를 만들고 prompt template을 저장합니다.
이후 Embedding Model로 Prompt Template 들의 임베딩을 생성합니다
def prompt_router(input):
query_embedding = embeddings.embed_query(input["query"])
similarity = cosine_similarity([query_embedding],prompt_embeddings)[0]
most_similar = prompt_templates[similarity.argmax()]
print("Using MATH" if most_similar == math_template else "Using PHYSICS")
return PromptTemplate.from_template(most_similar)
chain = (
{"query" : RunnablePassthrough()}
| RunnableLambda(prompt_router)
| ChatOpenAI(model = "gpt-3.5-turbo")
| StrOutputParser()
)
- 우선
prompt_router 함수는 사용자의 질문이 담긴 딕셔너리 객체를 입력으로 받고 해당 질문을 임베딩한다.
- 질문 임베딩과 template 임베딩을 비교해서 가장 비슷한 template을 PromptTemplate 객체로 만들어서 반환한다.
- 이후
RunnableLambda에 prompt_router 함수를 넣어서 chain을 구성한다.
따라서, query를 넣어서 invoke하면 질문과 관련이 높은 Prompt Template을 사용하여 자동으로 답변을 생성한다.
print(chain.invoke("What's a black hole"))
결과
Using PHYSICS
A black hole is a region in space where the gravitational pull is so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape from it. It is formed when a massive star collapses in on itself and the remaining mass is compressed into a very small space. The center of a black hole is called a singularity, where the laws of physics as we know them break down. Black holes can vary in size, with supermassive black holes found at the centers of galaxies and smaller stellar black holes formed from the remnants of massive stars.
print(chain.invoke("What's a path integral"))
결과
Using MATH
A path integral is a concept in mathematics and physics, specifically in the field of quantum mechanics. It involves integrating along all possible paths that a particle could take from one point to another, taking into account the probability amplitudes associated with each possible path. This approach allows for the calculation of quantum mechanical quantities such as the probability of a particle transitioning from one state to another. The mathematics behind path integrals can be quite complex, but they provide a powerful tool for understanding the behavior of particles at the quantum level.